
A word that came to everyone´s mind during the entire 2020 was climate change. News, magazines and journalists were discussing the issue on TV. But why? The consequences of climate change are being witnessed by us on earth. Extreme cold temperatures in winter, high hot temperatures on summer, droughts and insect outbreaks are some of them. What is the cause of climate change? The answer is easy: among other causes, the carbon cycle is being disturbed and its consequences are unstoppable. Carbon cycle and nitrogen cycle: what are them? Find it out here with easy and friendly words :)
Carbon cycle and nitrogen cycle are two extremely important nutrient cycles that occur in nature. What is the role of those cycles? Well, they regulate the species found in an ecosystem, how many of them are there and the seasonal changes they suffer through time.
Let´s first start with the definition of carbon. Carbon is a chemical and abundant element found on earth. It is an essential element for every form on earth, specially for living things (animals and plants). Carbon regulates temperature, it has a major role in the food we eat and it is a widely used element to boost our economy. The impressive characteristic about carbon is that it is continuously traveling from the atmosphere to the earth and back to the atmosphere again. Carbon is constantly moving in cycle between atmosphere and earth.
On earth, carbon is located in rocks and sediments. Apart from that, carbon is found in the atmosphere, in the ocean and in living organisms (plants and animals). When those living organisms die, carbon returns to the atmosphere again. Humans play a key role in the carbon cycle. The burning of fossil fuels and land damage carbon levels rise resulting in climate change and bigger consequences to the planet.
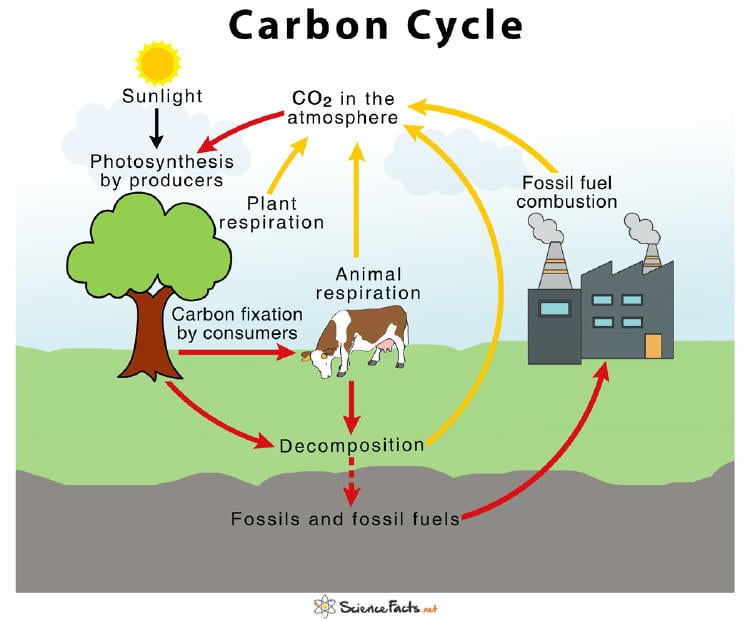
The carbon cycle is the way in which nature reuses carbon atoms around the environment: from atmosphere to earth and backwards. Discover how carbon cycle steps work below!
In this carbon cycle step, carbon moves rapidly from the atmosphere to plants attached to oxygen (C02). Plants absorb carbon dioxide through photosynthesis process. In that process, plants transform carbon dioxide coming from the atmosphere into oxygen (C02) and sugars which they use as food resulting in plant growth. Photosynthesis is a process that can be repeated forever! Plants pull out carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and they also serve as food to other living things.
In this step, carbon moves from plants into living animals. How does that happen? Well, animals eat plants so they incorporate carbon to their organisms. The explanation is food chain, the bigger living animals eat smaller living things :) As food chain continues, when an animal eats another animal, carbon continues to cycle. Let´s continue reading the carbon cycle steps.
What happens when plants and animals die? Animals' bodies and plants' leaves decay, as a result the carbon dioxide that was stored in them goes back to the soil. There is a possibility of dead animal bodies becoming fossil fuels in million years because they are buried in the ground. The bodies of plants and animals decompose, therefore carbon dioxide returns to the atmosphere :) Found more info in the next carbon cycle steps!
In this final step, the carbon dioxide moves from humans and other living things to the atmosphere. We, humans, are made of carbon! Imagine that most people eat plants and animals too, so carbon is great part of who we are. When we exhale air, we are releasing carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. That process is known as respiration. The carbon dioxide released in respiration returns to the atmosphere and can be used again in the process of photosynthesis. As we mentioned before, carbon cycles constantly.
Carbon enters into the atmosphere as carbon dioxide gas when we, humans, burn fuel fossils to use in factories, to power tracks and cars and more. As we mentioned at the beginning of the article, carbon dioxide gas is a pollutant. When cars and factories release carbon, the greenhouse effect is increased. Unfortunately, greenhouse gases contribute to climate change.
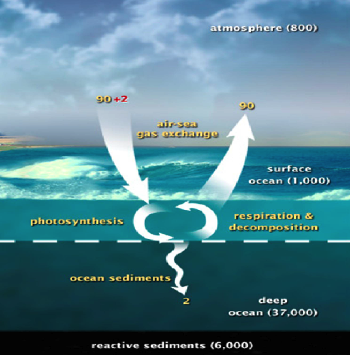
What is the role of oceans? Oceans basically absorb the carbon from the atmosphere, it is dissolved in water.
Now it is time to move on to the nitrogen cycle, as I mentioned above, both cycles are closely involved in the preservation of ecosystems and have a key role in nature. Nitrogen moves through living and non-living things. The nitrogen cycle is composed of the following steps:
Read this article to learn more about nitrogen and fertilizers: Organic Fertilizer: Take Care of your Plants with these Products
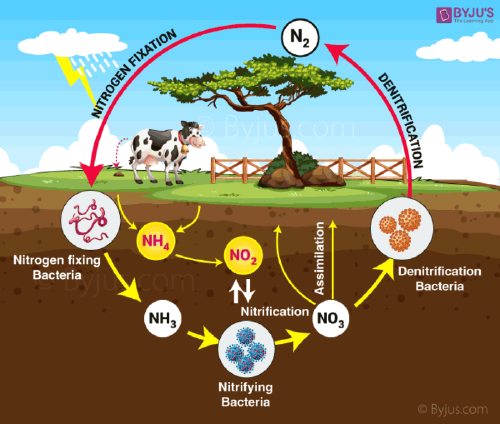
1. Nitrogen maintains the balance in ecosystems: the presence of plants and organic living material depends on the amount of nitrogen present in the environment. Understanding how the nitrogen cycle works, will led you to make thoughtful decisions regarding what are the ideal crops to plant in your soil.
2. Nitrogen is essential for our environment! It helps plant grow and also create protein in animals. At very low temperatures, nitrogen becomes liquid. In that state it is useful to keep food cool when they are transported for long distances.
3. The most important thing that I forgot to mention before is that nitrogen acts as a key element in the nucleic acids DNA and RNA. Those molecules are essential for living things. Find out what DNA and RNA are below!
We have finally reach to the end of this article! Carbon cycle and nitrogen cycle are important biogeochemical cycles in nature. They contribute for the balance in nature and ecosystems. Both elements are essential for sustaining life in the world. Without them, the world would be chaotic! Understanding their importance will help to be more conscious about the impact of our actions in the world.
Continue reading this article to learn how to upcycle and help the planet: Upcycling: A Way To Give Our Stuff A Second Chance.